Exploring the intricate connection between gut health and brain function, this article delves into the fascinating relationship that affects our overall well-being. From the microbiome to cognitive functions, prepare to uncover the secrets hidden within our bodies.
Detailing the significance of diet, probiotics, and prebiotics, this discussion aims to shed light on how our daily choices impact not just our gut but also our brain.
Introduction to Gut Health and Brain Function
Gut health refers to the balance and optimal functioning of the gastrointestinal system, including the microbiota present in the gut. It plays a crucial role in overall health and well-being, impacting various bodily functions.
The Gut-Brain Axis
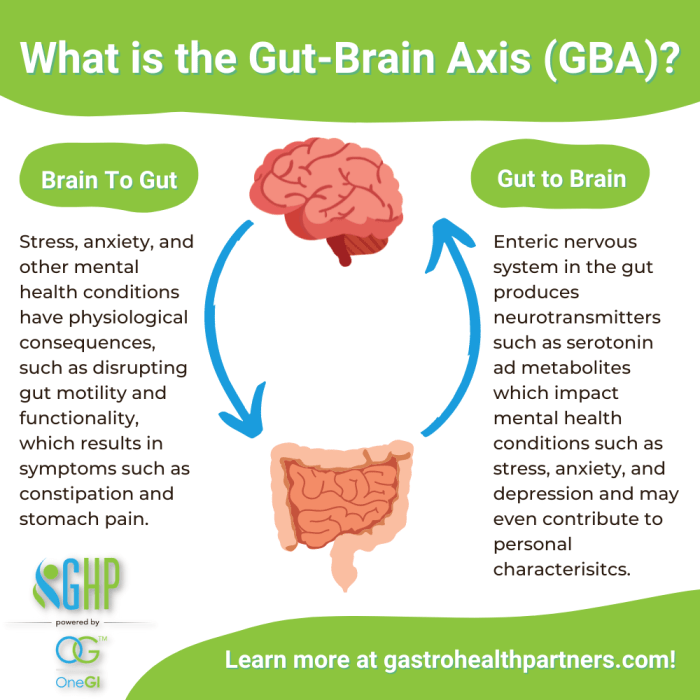
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system that links the gut and the brain. This connection allows for constant communication between the two, influencing various aspects of health, including immune response, metabolism, and cognitive functions.
- Gut Health Influences Mood: The gut microbiota produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, impacting mood regulation. An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
- Impact on Memory and Learning: Research suggests that the gut microbiota can influence cognitive functions like memory and learning. Healthy gut flora is essential for optimal brain function.
- Stress Response: The gut-brain axis plays a role in the body's response to stress. Chronic stress can disrupt gut health, leading to cognitive impairments and other mental health issues.
Components of Gut Health
Maintaining gut health is crucial for overall well-being, with various components playing important roles in this intricate system.
The Microbiome and its Significance in Gut Health
The gut microbiome refers to the diverse community of microorganisms residing in our digestive tract. These bacteria, fungi, and viruses play a vital role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. A balanced microbiome is essential for overall gut health, as an imbalance can lead to various health issues.
Impact of Diet on Gut Health and Brain Function
Diet plays a significant role in shaping the composition of the gut microbiome. A diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can negatively impact gut health, leading to inflammation and an imbalance in gut bacteria. This, in turn, can affect brain function, as the gut-brain axis connects the two organs through a complex network of communication pathways.
Role of Probiotics and Prebiotics in Maintaining a Healthy Gut
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore and maintain a healthy balance in the gut microbiome. They can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and kimchi, or taken as supplements. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for the good bacteria in the gut, promoting their growth and activity.
Including probiotic-rich foods and prebiotic fibers in your diet can support gut health and overall well-being.
Effects of Gut Health on Brain Function
Maintaining a healthy gut is not just important for digestion, but it also plays a crucial role in influencing brain function. The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system between the gut and the brain, impacting various aspects of mental health and well-being.
Mood and Mental Health
Poor gut health can lead to imbalances in the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for regulating mood. This imbalance can contribute to symptoms of depression and anxiety. Studies have shown that individuals with gastrointestinal issues are more likely to experience mood disorders
- Disruption in gut bacteria composition can affect the production of neurotransmitters.
- Inflammation in the gut can trigger inflammation in the brain, impacting mood regulation.
- Improving gut health through diet and probiotics has shown to have positive effects on mood disorders.
Relationship with Stress Response
The gut is sensitive to stress and can influence the body's response to stressful situations. Chronic stress can lead to changes in gut permeability, allowing toxins to enter the bloodstream and affect the brain. This can further exacerbate stress and anxiety levels.
Stress can alter the composition of gut microbiota, disrupting the balance and affecting overall gut health.
Conditions like Depression and Anxiety
There is a growing body of research linking gut health to conditions like depression and anxiety. The gut-brain axis plays a significant role in these mental health disorders, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy gut for overall well-being.
- Individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) often experience symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Studies have found a correlation between gut inflammation and the development of mood disorders.
- Improving gut health through lifestyle changes can have a positive impact on mental health outcomes.
Lifestyle Factors and Gut-Brain Connection
Maintaining a healthy gut is not just about what you eat; lifestyle factors like exercise, sleep, and stress management also play a crucial role in the gut-brain connection.
Exercise Influence on Gut Health and Brain Function
Regular exercise has been shown to promote a diverse microbiome in the gut, which is essential for overall gut health. This diversity can positively impact brain function by reducing inflammation and promoting the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, which is known as the "feel-good" hormone.
Impact of Sleep on the Gut-Brain Axis
Quality sleep is vital for the health of your gut and brain. During sleep, the body repairs and regenerates cells, including those in the gut lining. Disrupted sleep patterns can lead to an imbalance in gut bacteria and increase inflammation, affecting cognitive function and mood.
Stress Management Practices for Gut Health and Brain Function
Chronic stress can wreak havoc on your gut health and brain function. Implementing stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce inflammation in the gut, improve nutrient absorption, and support a healthier gut-brain axis.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the discussion on gut health and brain function opens doors to a new understanding of how our lifestyle choices can shape our mental well-being. By nurturing our gut, we might just be nurturing our brains too.
Top FAQs
How does gut health influence mood?
Gut health can impact mood through the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, often referred to as the "happy hormone."
Can stress affect gut health?
Yes, stress can disrupt the balance of bacteria in the gut, leading to issues like inflammation and digestive problems.
Are there specific foods that can boost gut health and brain function?
Foods rich in fiber, fermented foods, and those high in omega-3 fatty acids are known to promote a healthy gut and support brain function.
How does sleep impact the gut-brain axis?
Quality sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut-brain connection as it allows for proper regulation of various bodily processes.



![How to Cancel CarShield [Explained]](https://health.radartasik.id/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Carshield-Vs-Endurance-120x86.png)

